Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations wheres my second stimulus check of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Formula
- The Investment Decisions are a core area essential to strategic planning and financial management.
- If the NPV is positive, it indicates that the investment is expected to generate more cash flows than the initial investment and is therefore a good investment.
- This removes the time consuming element of working out the Net Present Value that has always been a deterrent.
- The calculation could be more complicated if the equipment were expected to have any value left at the end of its life, but in this example, it is assumed to be worthless.
- This means that you’ll make more in this investment than you would on interest if you put the same amount of money in the bank.
- CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path.
The higher the positive NPV, the more profitable the investment or project is likely to be. In this example, we are getting a positive net present value of future cash flows, so in this example also we will accept the project. The internal rate of return (IRR) is the discount rate at which the net present value of an investment is equal to zero.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
The Net Present Value tells you if your investment is likely to make a profit over a set period of time. But it does need initial definitions of its component parts, so it makes sense. Here are the other terms you need to get to the Net Present Value calculation. Net Present Value (NVP) is one of the ways to analyse an investment to see if it’s worth the risk.
Example 3: Bond Investment
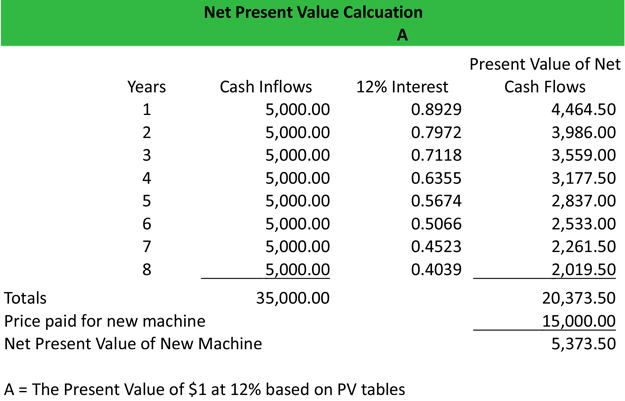
Once we have the total present value of all project cash flows, we subtract the initial investment on the project from the total present value of inflows to arrive at net present value. The net cash flows may be even (i.e. equal cash flows in different periods) or uneven (i.e. different cash flows in different periods). When they are even, present value can be easily calculated by using the formula for present value of annuity.
Sales Forecasting Methods
It means a rational investor would be willing to pay up to $61,466 today to receive $10,000 every year over 10 years. By paying this price, the investor would receive an internal rate of return (IRR) of 10%. By paying anything less than $61,000, the investor would earn an internal rate of return that’s greater than 10%. The first point (to adjust for risk) is necessary because not all businesses, projects, or investment opportunities have the same level of risk. Put another way, the probability of receiving cash flow from a US Treasury bill is much higher than the probability of receiving cash flow from a young technology startup. A conservative investor opts to purchase government bonds as part of a fixed-income strategy.
Using Cash Outflows to Determine NVP
For this reason, payback periods calculated for longer-term investments have a greater potential for inaccuracy. The full calculation of the present value is equal to the present value of all 60 future cash flows, minus the $1 million investment. The calculation could be more complicated if the equipment were expected to have any value left at the end of its life, but in this example, it is assumed to be worthless. Assume the monthly cash flows are earned at the end of the month, with the first payment arriving exactly one month after the equipment has been purchased. This is a future payment, so it needs to be adjusted for the time value of money. An investor can perform this calculation easily with a spreadsheet or calculator.
The discount rate used in NPV calculations is a critical factor in determining the result. A higher discount rate will result in a lower NPV, while a lower discount rate will result in a higher NPV. This is because a higher discount rate reflects a higher opportunity cost of investing in the project, while a lower discount rate reflects a lower opportunity cost.
When applying the net present value formula, you’re looking at whether revenues are greater than costs or vice versa to determine whether an investment or project is likely to yield a gain or a loss. NPV is sensitive to changes in the discount rate, which can significantly impact the results. Small changes in the discount rate can lead to large variations in NPV, making it challenging to determine the optimal investment or project. NPV is also applied in the valuation of securities, such as bonds, by calculating the present value of their future cash flows and comparing it to the current market price. A positive NPV indicates that the investment or project is expected to generate a net gain in value, making it an attractive opportunity.
Instead, they look at how long it will take for you to realize a return from an investment that’s equal to the dollar amount that you invested. Analysts use IRR or internal rate of return to evaluate proposed capital expenditures. The IRR calculation determines the percentage rate of return at which a project’s cash flows result in a net present value of zero. Say a fast-food chain is trying to decide whether to expand into a new market which entails opening up 10 more locations. They could calculate the net present value for each location, based on expected cash flows, to determine whether moving ahead with the project is a financially sound business decision. In the context of evaluating corporate securities, the net present value calculation is often called discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis.
To recap, the concept of time value of money says that getting $1 now is worth more than getting $1 sometime in the future. From the above result, we can be sure that this is a worthy investment; because the NPV of this new investment is positive. Here is the mathematical formula for calculating the present value of an individual cash flow.
The 5% rate of return might be worthwhile if comparable investments of equal risk offered less over the same period. It accounts for the fact that, as long as interest rates are positive, a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. For example, if a security offers a series of cash flows with an NPV of $50,000 and an investor pays exactly $50,000 for it, then the investor’s NPV is $0. Ideally, an investor would pay less than $50,000 and therefore earn an IRR that’s greater than the discount rate. For example, say Project A requires initial investment of $4 million to generate NPV of $1 million while a competing Project B requires $2 million investment to generate an NPV of $0.8 million.